Unit 7
Exploring a simple Python shell
In this session, you will create a command shell in Python, and then run it and answer questions about it. You can use your chosen Jupyter Notebook space for your work.
Review the blogs at Praka (2018) and Szabo (no date) and then create a CLI/ shell that implements the following:
- When you enter the command LIST it lists the contents of the current directory
- The ADD command will add the following two numbers together and provide the result
- The HELP command provides a list of commands available
- The EXIT command exits the shell
Add suitable comments to your code and add the program to your e-portfolio. Be prepared to demonstrate it in the seminar session next week.
Run the shell you have created, try a few commands and then answer the questions below. Be prepared to discuss your answers in the seminar.
- What are the two main security vulnerabilities with your shell?
- What is one recommendation you would make to increase the security of the shell?
- Add a section to your e-portfolio that provides a (pseudo)code example of changes you would make to the shell to improve its security.
The articles by Prakash (2018) and Gabor (no date) outline how to use the Python’s cmd library to implement an interactive command-line interface. To do so, it is enough to inherit the Cmd class and implement methods for the different commands. Below is the script implementing the requirements from the task and a demonstration of running multiple commands from the command line:
from cmd import Cmd
import os
class MyPrompt(Cmd):
prompt = '> '
intro = 'Welcome to the prompt! Type ? to list commands'
def do_exit(self, inp):
"""exit the application"""
print("Bye")
return True
def do_add(self, inp):
"""add two numbers together (usage: add number1 number2)"""
try:
# Split the input string and convert to numbers
args = inp.split()
if len(args) != 2:
print("Error: Please provide exactly two numbers")
return
num1 = float(args[0])
num2 = float(args[1])
result = num1 + num2
# If result is a whole number, convert to int for cleaner output
if result.is_integer():
result = int(result)
print(f"{num1} + {num2} = {result}")
except ValueError:
print("Error: Please provide valid numbers")
def do_list(self, inp):
"""list the contents of the current directory"""
files = os.listdir('.')
for file in files:
print(file)
def default(self, inp):
if inp == 'x' or inp == 'q':
return self.do_exit(inp)
return None
if __name__ == "__main__":
MyPrompt().cmdloop()
Welcome to the prompt! Type ? to list commands
> ?
Documented commands (type help <topic>):
========================================
add exit help list
> help add
add two numbers together (usage: add number1 number2)
> add 8.2 9.4
8.2 + 9.4 = 17.6
> list
.venv
main.py
.idea
The two possible vulnerabilities here are the absence of restrictions on listing files and directories in the current directory and probably issues with data sanitation.
The functionality to list files could potentially expose sensitive information or provide insight into the architecture of the system the script runs on. It is less relevant for an application run locally, but it could expose the architecture of a system in case of remote access and provide an attacker with insight into the possible attack methods.
The do_add() method implements basic value sanitation and will not interrupt the script execution even in case of providing invalid input. However, it could be easy to miss an edge case scenario when implementing multiple commands; that’s why it is crucial to perform extensive testing that would include providing various invalid input patterns in the command line.
References
Prakash, D. (2018) Write a shell in Python — Danish Prakash. Available at: https://danishpraka.sh/posts/shell-in-python/ (Accessed: 28 April 2025).
Python Software Foundation (2025) cmd — Support for line-oriented command interpreters, Python documentation. Available at: https://docs.python.org/3/library/cmd.html (Accessed: 18 July 2025).
Szabo, G. (no date) Create your own interactive shell with cmd in Python, Python programming language. Available at: https://python.code-maven.com/interactive-shell-with-cmd-in-python (Accessed: 28 April 2025).
Developing an API for a distributed environment
Using the Jupyter Notebook workspace, create a file named api.py and copy the following code into it (a copy is provided for upload to Codio/GitHub): You can install Jupyter Notebook on your local machine following these instructions or via the University of Essex Software Hub
source of code: Codeburst
from flask import Flask
from flask_restful import Api, Resource, reqparse
app = Flask(__name__)
api = Api(app)
users = [
{
"name": "James",
"age": 30,
"occupation": "Network Engineer"
},
{
"name": "Ann",
"age": 32,
"occupation": "Doctor"
},
{
"name": "Jason",
"age": 22,
"occupation": "Web Developer"
}
]
class User(Resource):
def get(self, name):
for user in users:
if(name == user["name"]):
return user, 200
return "User not found", 404
def post(self, name):
parser = reqparse.RequestParser()
parser.add_argument("age")
parser.add_argument("occupation")
args = parser.parse_args()
for user in users:
if(name == user["name"]):
return "User with name {} already exists".format(name), 400
user = {
"name": name,
"age": args["age"],
"occupation": args["occupation"]
}
users.append(user)
return user, 201
def put(self, name):
parser = reqparse.RequestParser()
parser.add_argument("age")
parser.add_argument("occupation")
args = parser.parse_args()
for user in users:
if(name == user["name"]):
user["age"] = args["age"]
user["occupation"] = args["occupation"]
return user, 200
user = {
"name": name,
"age": args["age"],
"occupation": args["occupation"]
}
users.append(user)
return user, 201
def delete(self, name):
global users
users = [user for user in users if user["name"] != name]
return "{} is deleted.".format(name), 200
api.add_resource(User, "/user/<string:name>")
app.run(debug=True)
Question 1
Run the API.py code. Take a screenshot of the terminal output. What command did you use to compile and run the code?
The python script is run by using the following command:
python API.py
The result of the execution is below:
* Serving Flask app 'API'
* Debug mode: on
WARNING: This is a development server. Do not use it in a production deployment. Use a production WSGI server instead.
* Running on http://127.0.0.1:5000
Press CTRL+C to quit
* Restarting with stat
* Debugger is active!
* Debugger PIN: 413-777-398
Question 2
Run the following command at the terminal prompt: w3m http://127.0.0.1:5000/user/Ann
What happens when this command is run, and why?
Instead of w3m, the built-in HTTP Client in PyCharm is used to send requests to the server.
GET http://127.0.0.1:5000/user/Ann
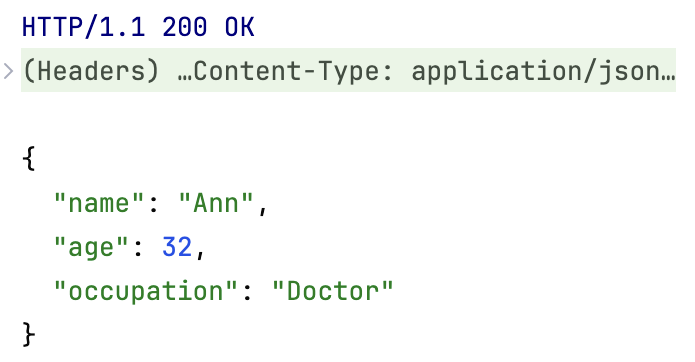
The server executes the get() method of the User resource, finds the user with the matching name in the users collection and returns it.
Question 3
Run the following command at the terminal prompt: w3m http://127.0.0.1:5000/user/Adam
What happens when this command is run, and why?
GET http://127.0.0.1:5000/user/Adam
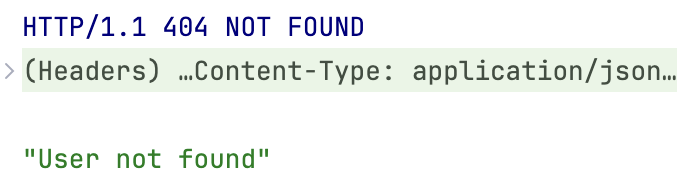
The server responds with an error status as described in the get() method for the case there is no match in the list of users:
def get(self, name):
for user in users:
if name == user["name"]:
return user, 200
return "User not found", 404
Question 4
What capability is achieved by the flask library?
The flask library in this example provides diverse functionality for implementing a web server:
- Sets up the HTTP server to handle HTTP requests;
- Provides a framework for implementing RESTful APIs thanks to the
flask_restfullibrary; - Provides resource-based routing: the API maps various endpoints to the corresponding resources and HTTP methods (
GET,POST, etc.); - Implements requests’ parsing with
reqparse.
The library seems to provide the necessary basic functionality for implementing a server application.